Configuring shell colours
Whilst moving my development environment to WSL2, I noticed that the default shell colours for listing files made the text hard to read due to poor contrast. So I went about finding a way to change those defaults.
This guide was written using Ubuntu via WSL2.
First let's look at our current output of ls -la.
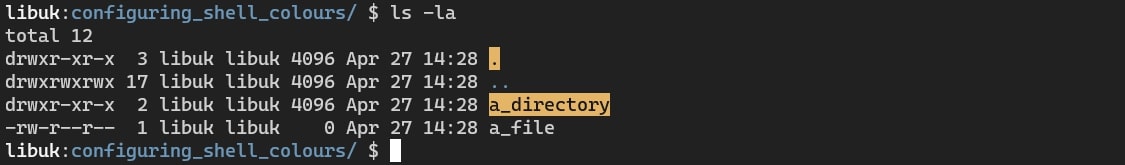
Here we can see the a_directory directory is presented with a
yellow and background and black text.
LS_COLORS
The ls program reads from the LS_COLORS variable to determine
how the filenames will be displayed in the terminal. This variable
can be set using the dircolors program. You can read more about
it on its man page.
The LS_COLORS variable can be set directly, but for the purpose
of this guide we'll be using dircolors. Here's a solution
for using LS_COLORS directly.
Creating our dircolors config file
We can save the output of the dircolors program to create a
config file.
dircolors -p > $HOME/.dircolors
We call run the dircolors program with the -p flag which is
short for --print-database. This will give us a list of
currently configured settings, and we write the output to our
config file .dircolors.
Here we save the file in our home directory, but you can save yours in whatever location you prefer.
We want our shell to load our new config instead of loading the
default. Let's add some code to our .bashrc (or .zshrc if
you're using zsh like I am) that will run on startup.
# dircolors - load config for ls colors
dircolors_config=$HOME/.dircolors
test -r $dircolors_config && eval "$(dircolors $dircolors_config)"
This snippet checks for the existence of a file .dircolors in
the home directory, be sure to point yours to the location you
saved it if you chose another location. It then passes that file
as an argument to the dircolors program which sets the
LS_COLORS variable.
Setting colours
Open the .dircolors file in your preferred text editor. We have
some comments describing each section, and we can see some colour
code definitions we can use to customise it ourselves.
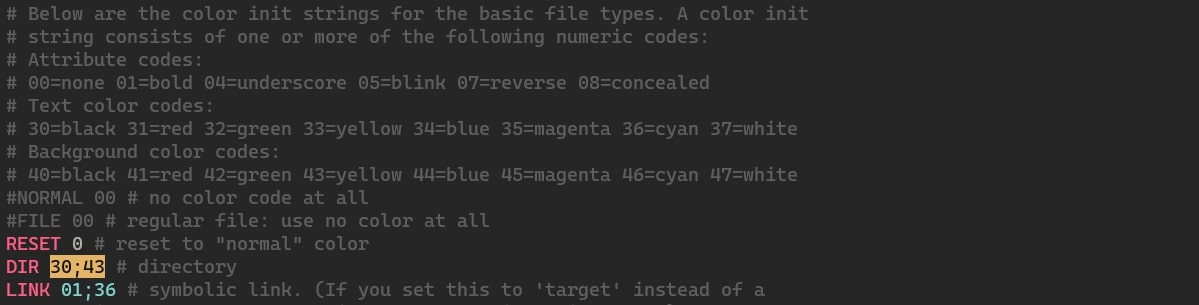
If we want to set the background colour for a directory to white, first we find the existing statement and make our changes. In my case it's set to yellow.
DIR 30;43Let's change the background from yellow to white.
DIR 30;47And the text colour from black to red
DIR 31;47The syntax represents the following entities separated by a semicolon in the following order.
- DIR - we're setting a color for directories
- 31 - the text color code, which is set to red
- 47 - the background color code, which is set to white
Let's load our new config by using the source program.
source ~/.zshrc
When we now run ls -la the colour of directories should have now
changed.
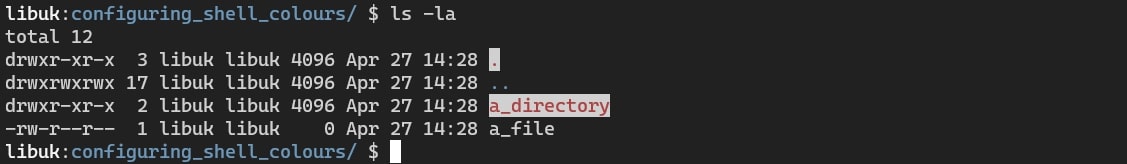
There we have it! How to customise the output of ls without any
extra tools or themes. Experiment and customise to your hearts
content.